How Might You Determine Whether It Was A Plant Cell Or An Animal Cell

Differences between Plant and Animal Cells: Plants and Animals consist the major kingdoms of Domain Eukarya. On the i mitt, Kingdom Plantae is composed of multi-cellular (although some are unicellular) autotrophic organisms. At present, it is estimated that the total number of plants is 400,000 while of grade, a lot remains undiscovered.
On the other hand, the members of the Kingdom Animalia make up more than three-fourths of all species found on our planet. They typically range from the simplest, like the sponges and corals, up to the most adult i like humans.
Regarding physical appearance, plants undeniably are distinctly different from animals. Merely what about inside them? Exercise they differ as well? Well, in this post, nosotros volition explore the respond to that question!
We volition discuss establish cell vs animal cell, everything at the cellular organization level. Check out the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells as well.
Table of Contents
- What are Plant Cells?
- Types of Constitute Cells
- 1. Parenchyma
- 2. Collenchyma
- 3. Sclerenchyma
- 4. H2o Conducting Cells
- 5. Sieve Tube Members
- What are Animate being Cells?
- Types of Brute Cells
- one. Nerve Cells
- two. Claret Cells
- iii. Muscle Cells
- 4. Skin Cells
- 5. Bone Cells
- What Are The Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells?
![]()
What are Plant Cells?
Like any other eukaryotic cells, plant cells that accept their genetic cloth enclosed in the nucleus and accept membrane-bound organelles. One of the most distinctive features of plants cells is the presence of cell wall apart from the cell membrane itself.
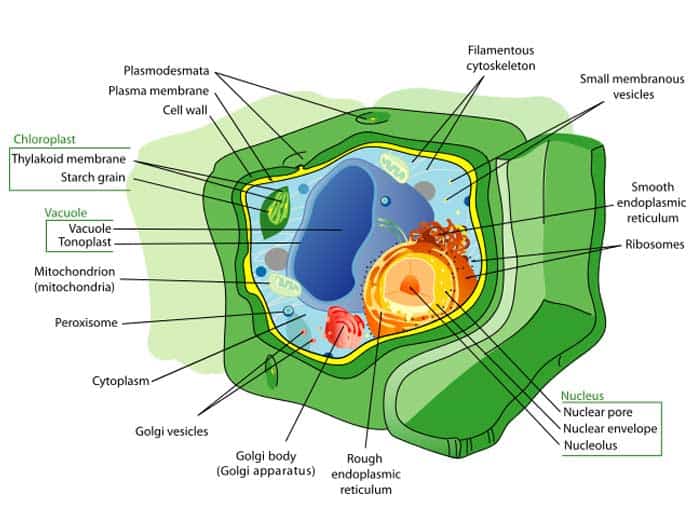
- This jail cell wall, primarily composed of cellulose, is what provides the whole plant structure support and rigidity.
- The primary function of plant cells is to carry out photosynthesis because of the presence of chlorophyll in their chloroplasts.
- It was once believed that institute cells originated from the endosymbiosis between a single-celled photosynthetic organism and a larger proto-eukaryote.
![]()
Types of Plant Cells
Different types of found cells are specific in performing certain functions necessary for survival. The post-obit are the types of plant cells:
-
ane. Parenchyma
Among all types of found cells, parenchyma cells are the simplest in terms of construction – they only accept thin walls. These cells are not highly specialized a primarily used for the storage of organic products.
-
2. Collenchyma
Collenchyma cells accept relatively sparse walls only with some degrees of thickening at some parts of the cell. This type of construction allows the constitute prison cell to utilize their function as structural support.
-
3. Sclerenchyma
Unlike parenchyma and collenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells have highly lignified (embedded with lignin) jail cell walls which are thickened expressionless cells at maturity.
-
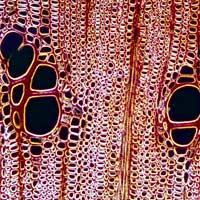
4. Water Conducting Cells
Xylem is a plant vascular tissue which helps in transmitting water from roots to all parts of the constitute. The cells in this tissue have a hardening agent, unlike collenchyma cells. There are two types of cells inside Xylem namely tracheids and vessel members. Seedless vascular plants contain tracheids whereas flowering plants (Angiosperms) contain both tracheids and vessel members.
-

5. Sieve Tube Members
Phloem is another institute tissue which is responsible for conducting foods produced (via Photosynthesis) in the leaves to all parts of the establish. Within this tissue, 3 types of cells found namely companion cells, phloem fibers, and parenchyma cells.
![]()
What are Animate being Cells?
Animal cells are also a blazon of eukaryotic cells that contain a "true nucleus" and membrane-jump organelles enclosed together past a plasma membrane.
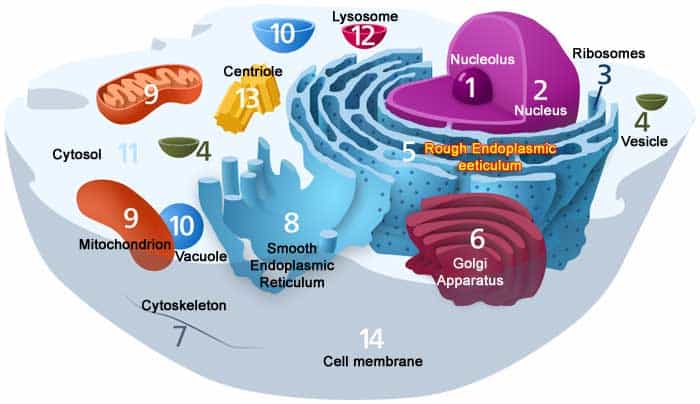
- Brute cells do not have a prison cell wall, which typically distinguishes them from other eukaryotic organisms like plants and fungi.
- Scientists believed that the characteristic of having prison cell wall by animals is a feature that was lost in the by by a single-celled organism that eventually gave rise to the Kingdom Animalia.
- Despite the lack of a rigid cell wall, animal cells have developed a broad array of prison cell types, tissues, and organs. Animal cells typically evolved to form nerves and muscles which allowed them for locomotion and mobility.
- While beingness mobile has greatly immune animals to do a lot of things, creature cells per se are unable to synthesize their ain food, hence are always dependent on plants.
![]()
Types of Animal Cells
There are unlike types of animals per se, depending on the type of environment they live in and their lifestyle. However, listed below are some of the almost common types of beast cells.
-
one. Nerve Cells
Nervus cells are specialized cells that electro-chemically send impulses or information to and from the sensory receptors and the key nervous system.
-
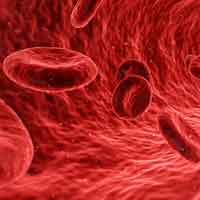
ii. Blood Cells
Also chosen equally the hematopoietic cell, the blood cell is responsible for conveying oxygen to the different tissues while at the same time collecting carbon dioxide from them. Aside from that, claret cells also bring with them hormones and other nutrients and transport them to the unlike parts of the body.
-
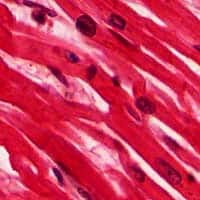
3. Muscle Cells
Muscle cells, also called myocytes, are long and tubular cells (sometimes spindle-shaped) that function for the product of force and movement. In animals, musculus cells contain the nearly number of mitochondria.
-
4. Pare Cells
Located in the epidermal and dermal layer, skin cells function mainly for protection, perception, and manual of sensation. In addition to that, pare cells likewise foreclose water loss through dehydration.
-
5. Bone Cells
Os cells make up the bones and overall skeleton of animals. While there are unlike types of bone cells, their principal role is to provide structural support and assistance in movement.
![]()
What Are The Differences Between Plant and Brute Cells?
As eukaryotic cells, plants and brute cells share many features in common, including organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, cell membrane, and others. However, as both are fundamental units of entities, each has its own feature differentiating information technology from the other. Here are the 17 differences in animal and plant cells:
![]()
Cite This Folio
Source: https://www.bioexplorer.net/difference-between-plant-and-animal-cells.html/
Posted by: lairdobler1999.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Might You Determine Whether It Was A Plant Cell Or An Animal Cell"
Post a Comment